相交链表
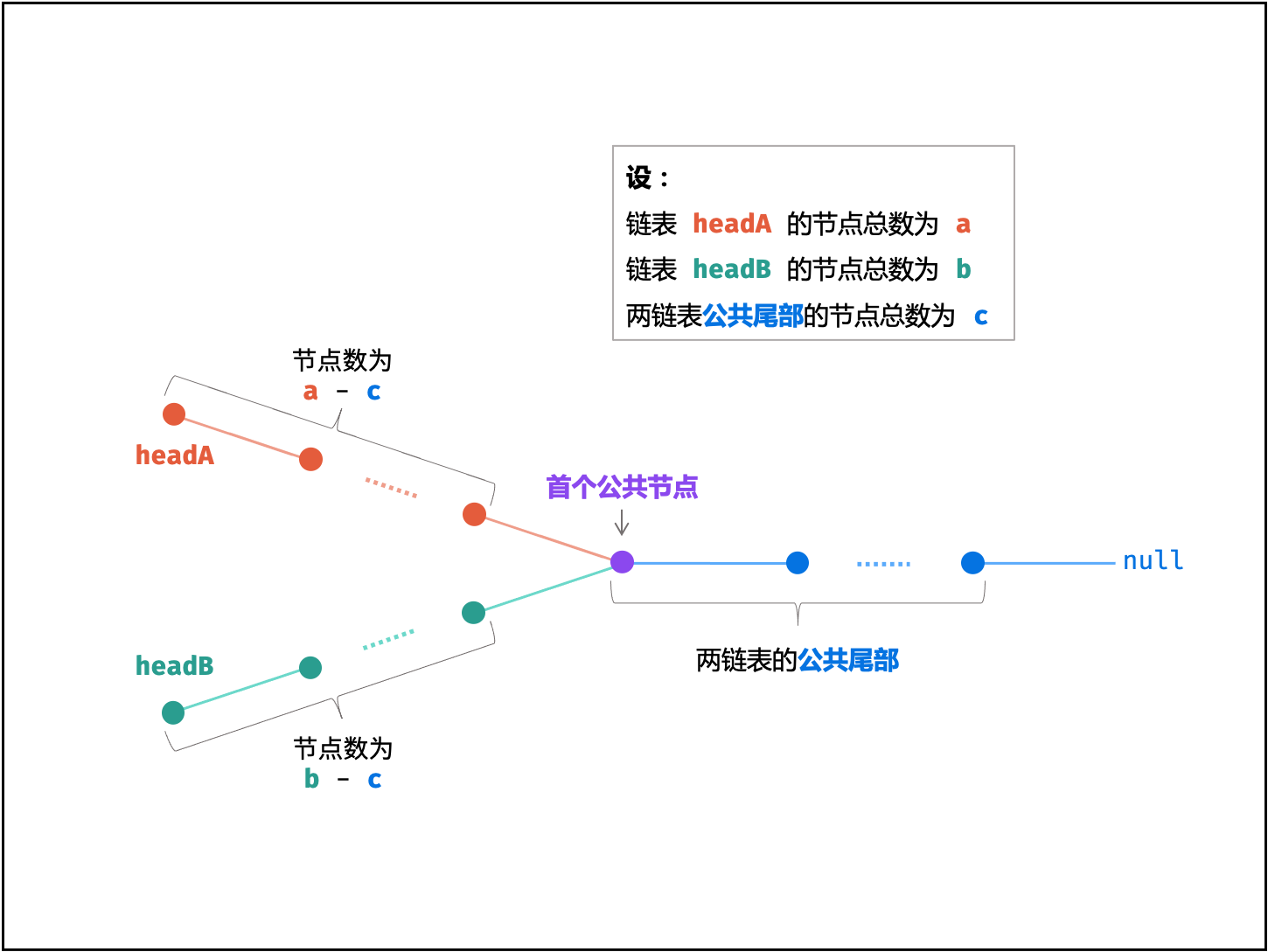
假设链表1: A = [1 2 7 8 9] 链表2: B = [6 7 8 9]
连接链表: 从后端可看出,结尾处链表相交,且所在位置相同
AB = [1 2 7 8 9 0 6 7 8 9 0]
BA = [6 7 8 9 0 1 2 7 8 9 0] 0的由来:结点定义node->next = null
由于最后一个结点为0,所以比较到最后必然结束
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode *A = headA, *B = headB;
while (A != B) {
A = A != nullptr ? A->next : headB;
B = B != nullptr ? B->next : headA;
}
return A;
}
};
作者:Krahets
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/solutions/12624/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-shuang-zhi-zhen-l/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
反转链表(递归)
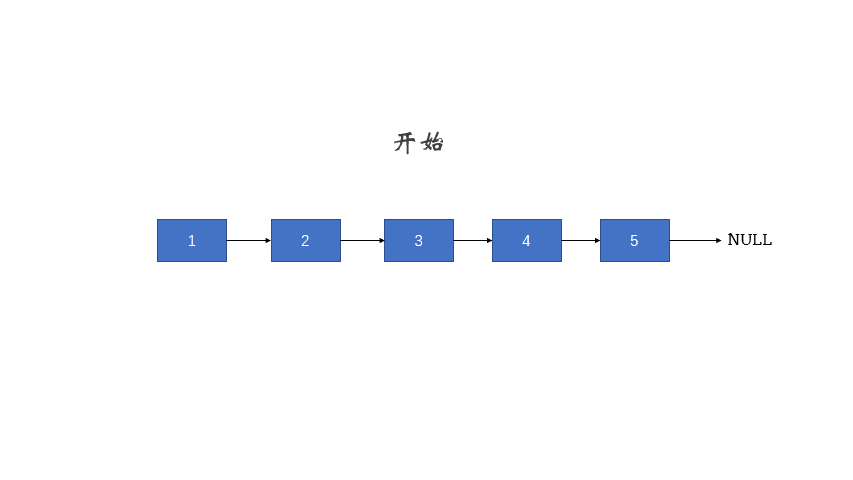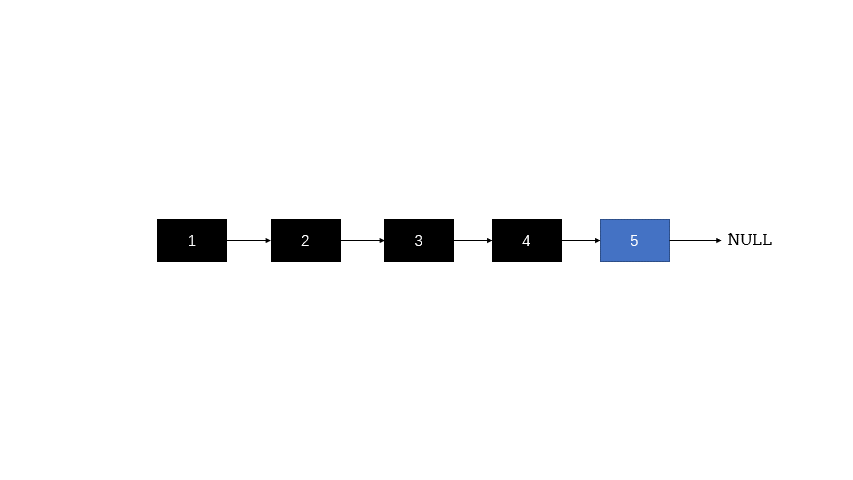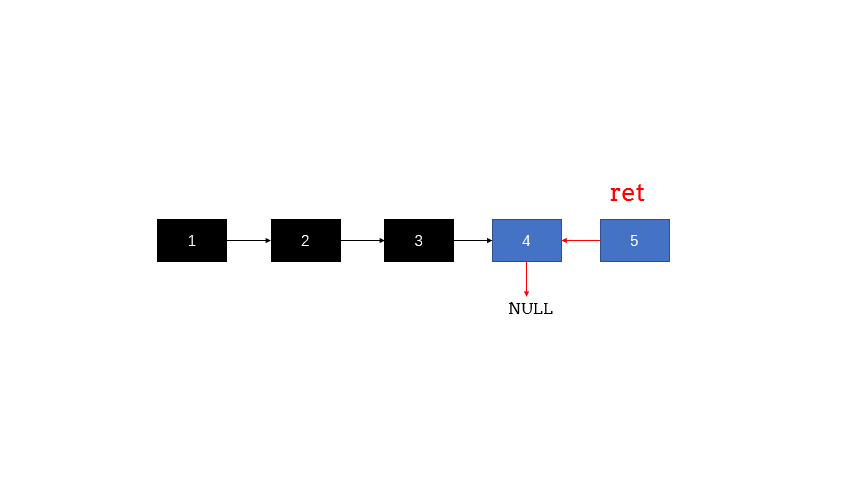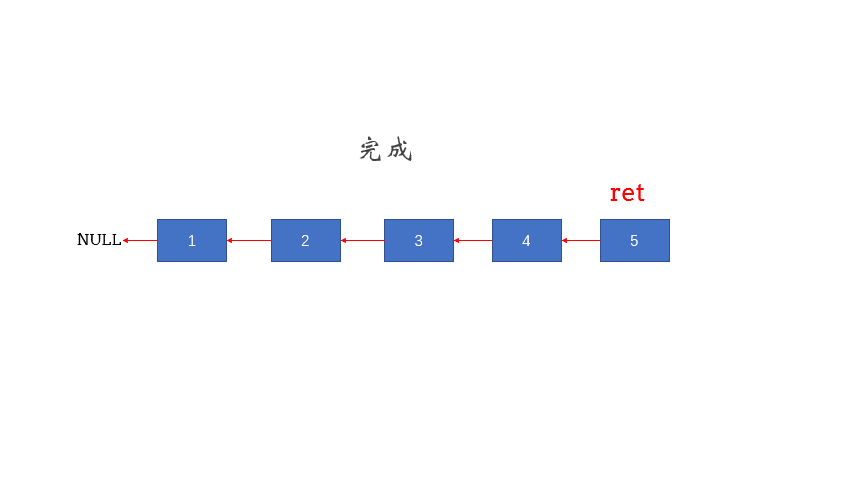
设计递归
- 结束条件 head->next == null
- 返回值 头节点ret
- 递归循环操作:反转结点
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) { //结束条件
return head;
}
ListNode *ret = reverseList(head->next); //返回值
head->next->next = head; //递归操作
head->next = nullptr; //此处设为null原因为设置末尾结点
return ret;
}
};
回溯算法(组合)
// list = {1, 2, 3} 所需排列组合的列表
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 1 3
2 3 1
3 1 2
3 2 1
// visited 标记数组元素是否已访问
// path 保存排列结果
void backtracking(vector<int> &list, vector<bool> &visited, vector<int> &path) {
if (path.size() == list.size()) { // 输出结果
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); i++) {
cout << path[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (visited[i]) continue; // 跳过已访问元素
visited[i] = true;
path.push_back(list[i]);
backtracking(list, visited, path); // 该元素下一层
visited[i] = false;
path.pop_back();
}
}
迷宫问题(寻找可达路径数量)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// global const
int total_way = 0;
int dir[4][2] = {{0,1}, {1,0}, {0,-1}, {-1,0}};
// global variety
pair<int, int> end1;
void dfs(vector<vector<int>> &matrix, vector<vector<bool>> &visited, int x, int y);
int main() {
// initial the size of matrix
int n, m, num;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> matrix(n+2, vector<int>(m+2, 0));
vector<vector<bool>> visited(n+2, vector<bool>(m+2, false));
for(int i=1; i<n+1; i++) {
for(int j=1; j<m+1; j++) {
cin >> num;
matrix[i][j] = num;
}
}
// end1 position
cin >> end1.first >> end1.second;
// DFS
dfs(matrix, visited, 1, 1);
cout << total_way << endl;
return 0;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>> &matrix, vector<vector<bool>> &visited, int x, int y) {
// Termination Condition
if(matrix[x][y] == 0 || visited[x][y]) return;
if(x == end1.first && y == end1.second) {
total_way++;
return;
}
// Loop
visited[x][y] = true;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int nx = x + dir[i][0];
int ny = y + dir[i][1];
dfs(matrix, visited, nx, ny);
}
visited[x][y] = false;
return;
}
关键点:
- visited的标记位置(判断合法后为true,结束Loop后为false)
